SUCTION MACHINE- KENYA
Suction Machine is an appliance used to remove substances such as blood, saliva, mucus and vomit from a person’s airway.
Working Principle
It works by atmospheric pressure, when the piston is raised creating a partial vacuum, atmospheric pressure outside forces water into the cylinder hence it is permitted to escape by an outlet valve.
Oil free lubrication pump to keep the environment from being polluted by the oil mist.
low noise
Square negative pressure meter and plastic cover.
no any negative pressure to be generated during running to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Negative pressure regulating system can be adjusted steplessly small in size, light in weight and portable
KSh 20,000.00
CompareA suction machine two bottle, a device that is used to remove substance
such as blood, saliva, mucus and vomit from a person’s airway.
Related products
-
Uncategorized, Home Care Equipment, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT, OPERATING THEATRE EQUIPMENT, Oxygen Concentrator-Kenya
PORTABLE OXYGEN CONCENTRATOR 5LTS
 Uncategorized, Home Care Equipment, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT, OPERATING THEATRE EQUIPMENT, Oxygen Concentrator-Kenya
Uncategorized, Home Care Equipment, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT, OPERATING THEATRE EQUIPMENT, Oxygen Concentrator-KenyaPORTABLE OXYGEN CONCENTRATOR 5LTS
0 out of 5(0)Portable Oxygen Concentrator
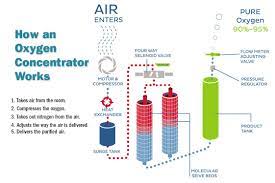
It is a medical device that assist people who have low level of oxygen in their blood. they are powered by plugging the device into an electrical outlet or by using a battery.
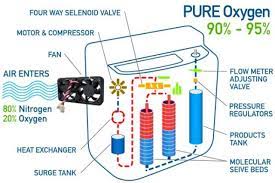
Steps of concentrator process
- Takes air from the room
2. Compresses the oxygen
3. Takes out nitrogen from the air
4. Adjust the way the air is delivered
5. Delivers the purified air to the patient
 SKU: n/aKSh 70,000.00
SKU: n/aKSh 70,000.00 -
Home Care Equipment, HOSPITAL BEDS, Hospital Furniture, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
Electric 3 Function Hospital Bed- Kenya
 Home Care Equipment, HOSPITAL BEDS, Hospital Furniture, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
Home Care Equipment, HOSPITAL BEDS, Hospital Furniture, MEDICAL EQUIPMENTElectric 3 Function Hospital Bed- Kenya
0 out of 5(0)It is ideal for home patient use, users are able to adjust the back leg and height adjustment for better comfort. Low in power consumption and only consume when the remote is on.
With three controls, the electrical hospital bed is able to perform the following base function.
- Back raise
- Leg raise
- Height adjustment
SKU: n/aKSh 150,000.00KSh 200,000.00 -
Black Friday, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
FINGER TIP PULSE OXIMETER
0 out of 5(0)Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring a person’s oxygen saturation. Though its reading of peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) is not always identical to the more desirable reading of arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) from arterial blood gas analysis, the two are correlated well enough that the safe, convenient, noninvasive, inexpensive pulse oximetry method is valuable for measuring oxygen saturation in clinical use.
In its most common (transmissive) application mode, a sensor device is placed on a thin part of the patient’s body, usually a fingertip or earlobe, or in the case of an infant, across a foot. The device passes two wavelengths of light through the body part to a photodetector. It measures the changing absorbance at each of the wavelengths, allowing it to determine the absorbances due to the pulsing arterial blood alone, excluding venous blood, skin, bone, muscle, fat, and (in most cases) nail polish.
Reflectance pulse oximetry is a less common alternative to transmissive pulse oximetry. This method does not require a thin section of the person’s body and is therefore well suited to a universal application such as the feet, forehead, and chest, but it also has some limitations. Vasodilation and pooling of venous blood in the head due to compromised venous return to the heart can cause a combination of arterial and venous pulsations in the forehead region and lead to spurious SpO2 results. Such conditions occur while undergoing anesthesia with endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation or in patients in the Trendelenburg position.
SKU: n/aKSh 1,500.00 -
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
E.N.T Diagnostic Set
0 out of 5(0)A diagnostic set consist of an ophthalmoscope for examining the eye, an otoscope for examining the tympanic membrane and external ear canal and a battery handle to power these instrument
a complete ENT examination includes: inspection of the face, ears, nose, throat and neck
SKU: n/aKSh 8,500.00



