SUCTION MACHINE- KENYA
Suction Machine is an appliance used to remove substances such as blood, saliva, mucus and vomit from a person’s airway.
Working Principle
It works by atmospheric pressure, when the piston is raised creating a partial vacuum, atmospheric pressure outside forces water into the cylinder hence it is permitted to escape by an outlet valve.
Oil free lubrication pump to keep the environment from being polluted by the oil mist.
low noise
Square negative pressure meter and plastic cover.
no any negative pressure to be generated during running to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Negative pressure regulating system can be adjusted steplessly small in size, light in weight and portable
KSh 20,000.00
CompareA suction machine two bottle, a device that is used to remove substance
such as blood, saliva, mucus and vomit from a person’s airway.
Related products
-
Christmas Offer, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
Portable Nebulizer
0 out of 5(0)A nebulizer turns liquid medicine into a mist, it is portable, electric version.
Made up of a base that holds an air compressor, small container for the liquid medicine and a tube that connects the air compressor to the medicine container.
Above the medicine container is a mouth piece or a mask you use to inhale the mist.
Ideal to use when you are having an asthma attack, can be used with younger children.
SKU: n/aKSh 5,000.00KSh 6,500.00 -
Black Friday, BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORS, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
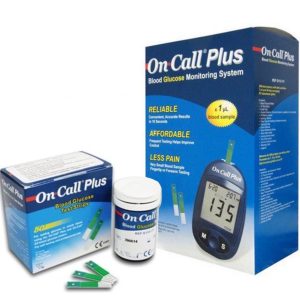
On Call Plus Blood Glucose Monitoring System
 Black Friday, BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORS, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
Black Friday, BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORS, MEDICAL EQUIPMENTOn Call Plus Blood Glucose Monitoring System
0 out of 5(0)On-Call Plus – blood glucose meter from Alpha Surgicals Supplies Ltd.
Accurate and reliable.Easy to use.For encoding, a special chip from a set of test strips is used.
Analysis time 10 seconds.
The minimum drop of blood – 1mkl.
The possibility of drawing blood from the palm and forearm, which greatly simplifies the life of the fingertips.
Memory for 300 results, an average of 7, 14 and 30 days.
The power supply uses a standard CR2032 battery with a resource of up to 1000 measurements and a power loss warning system. This allows you not to worry that the battery will sit at the most inopportune moment. Order this machine from ALPHA SURGICALS SUPPLIES LTD, NAIROBI…Free delivery within CBD.Package includes:
On Call ® Plus System Finger piercing pen (lanceolate device)Sterile lancets – 10 pcs.Test strips – 10 +150 pcs.Coding chip Cover for storage and transportation Replaceable cap lanceolate device for taking samples from alternative locations.Control solution User’s Manual.Diary of self-control.Battery.Warranty card.SKU: n/aKSh 4,000.00 -
LAMPS, MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
Infrared Heating Lamp With Stand
0 out of 5(0)Infrared heating lamp with stand
IR lamp is a high quality heat lamp designed to provide localized heat treatment.
Manage pain and injury effectively heat therapy provides benefits for numerous injuries, illness and chronic conditions.
The heat lamp uses short-wave infrared light produced by an incandescent heat sources to give a deeper penetration of heat than conventional heat sources.
This can enhance blood circulation improving the transport rate of essential biochemical compounds as well as provide pain relief and a pleasant warming effective exposure.
Heat therapy for home or business it is ideal for us at home or in a professional setting.
SKU: n/aKSh 17,000.00