Laboratory Equipment
Laboratory Equipment,
These are equipment used in laboratory room,
It might be for medical purpose or research. when choosing for a laboratory equipment make sure you get a quality and affordable.
Without further ado lets jump in and learn more about different types of lab equipment and their function;
- Microscope: This is a unique type of a binocular that is used to view molecules that ca not be viewed by naked eye, we have two types of microscope (A) Light and (B) Electron. as the name suggest, light microscope uses natural light to magnify images of small object Binocular
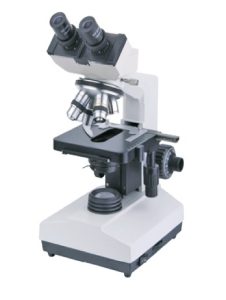 are the most common used.
are the most common used. - Centrifuge: It is a device that uses centrifugal force to separate different component in a solution, works by using the principle of sedimentation: Under the influence of gravitational force (g-force), substances separate according to their density. … Protocols for centrifugation typically specify the relative centrifugal force (rcf) and the degree of acceleration in multiples of g (g-force).
- Autoclave: It is a machine that is used to sterilize surgical instrument, it uses steam to kill all bacteria and viruses, it comes in different liters according to the usage.
How it works;
- The autoclave works on the principle of moist heat sterilization where steam under pressure is used to sterilize the material present inside the chamber.
- The high pressure increases the boiling point of water and thus helps achieve a higher temperature for sterilization.
- Water usually boils at 100°C under normal atmospheric pressure (760 mm of Hg); however, the boiling point of water increases if the pressure is to be increased.
- Similarly, the high pressure also facilitates the rapid penetration of heat into deeper parts of the material, and moisture present in the steam causes the coagulation of proteins causing an irreversible loss of function and activity of microbes.
- This principle is employed in an autoclave where the water boils at 121°C at the pressure of 15 psi or 775 mm of Hg.
- When this steam comes in contact on the surface, it kills the microbes by giving off latent heat.
- The condensed liquid ensures the moist killing of the microbes.
- Once the sterilization phase is completed (which depends on the level of contamination of material inside), the pressure is released from the inside of the chamber through the whistle.
- The pressure inside the chamber is then restored back tot eh ambient pressure while the components inside remain hot for some time.
